From roughly 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization was one of the earliest and most developed ancient societies. It was mostly in what is now Pakistan and India, northwest of the Indian peninsula. Many interesting facts about the Indus valley civilization, including a rich cultural legacy, are still being studied today.
So, what is unique about the Indus Valley Civilization? The following information sheds light on this intriguing old civilization.
Advanced Urban Planning and Architecture
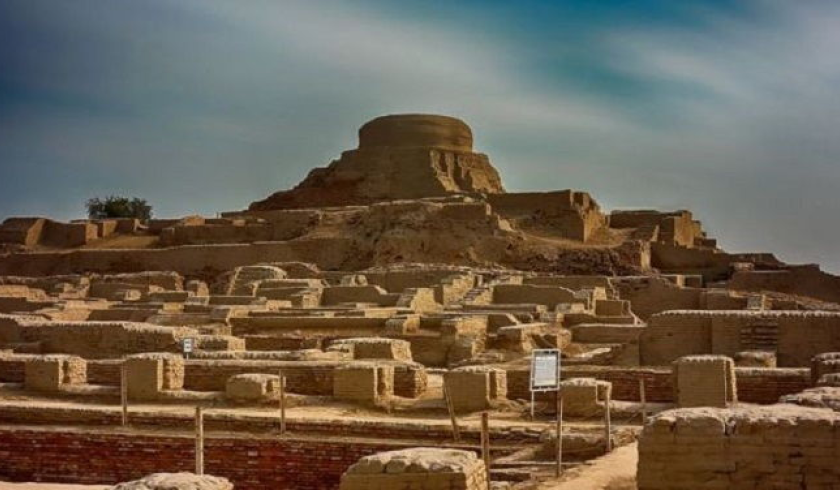

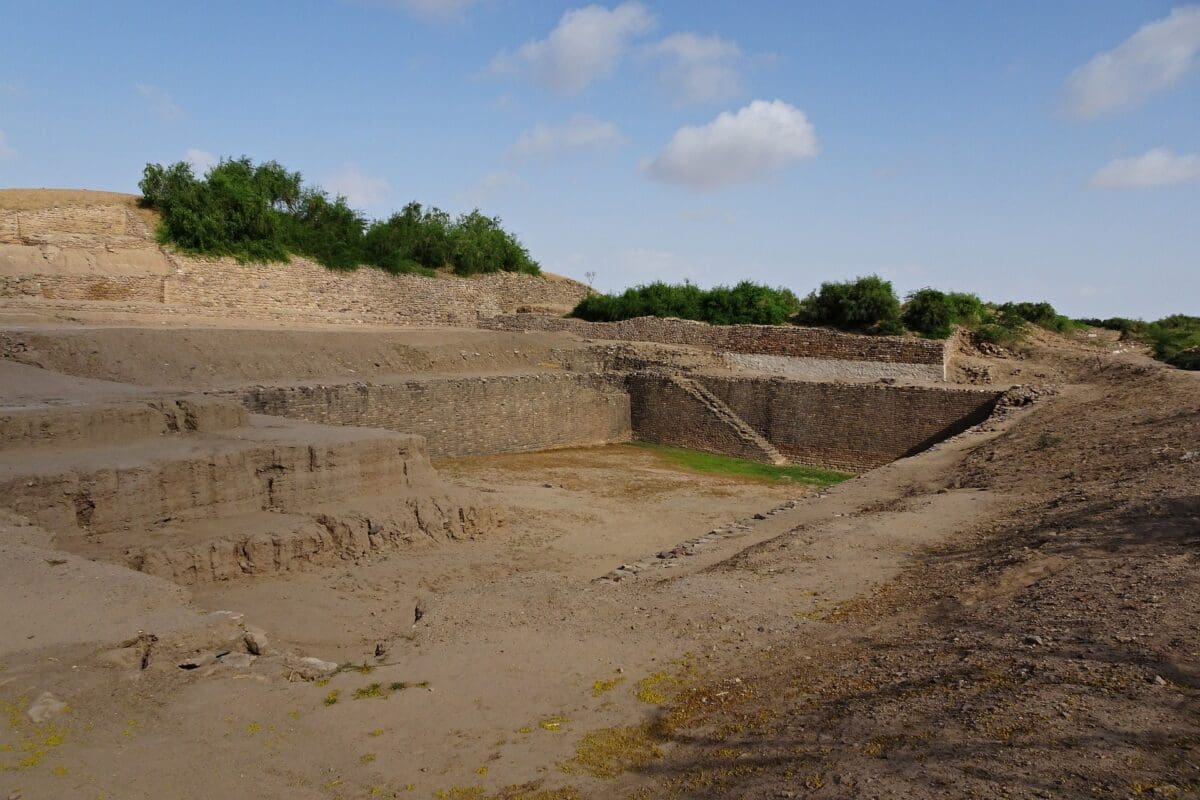
Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were two of the Indus Valley Civilization’s largest and most important cities. They were distinguished by their cutting-edge urban design and construction. The buildings were made of baked brick with flat roofs, and the streets were grid-like.
One of the interesting facts about Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro was that they had sophisticated drainage systems, proving the civilization’s superior engineering abilities. Additionally, there were public restrooms and wells with pure water for drinking and bathing.
Sophisticated Writing System
The writing system used by the Indus Valley Civilization has yet to be understood entirely. The characters are thought to symbolize words or ideas, but their exact meaning is still unknown. “The Indus Script: Texts, Concordance, and Tables” by Asko Parpola and Iravatham Mahadevan provides a comprehensive analysis of the Indus script and includes a catalog of all known inscriptions, as well as tables and concordances for studying the writing.
Thanks to recent technological developments, the script can now be examined more closely.
Advanced Agriculture
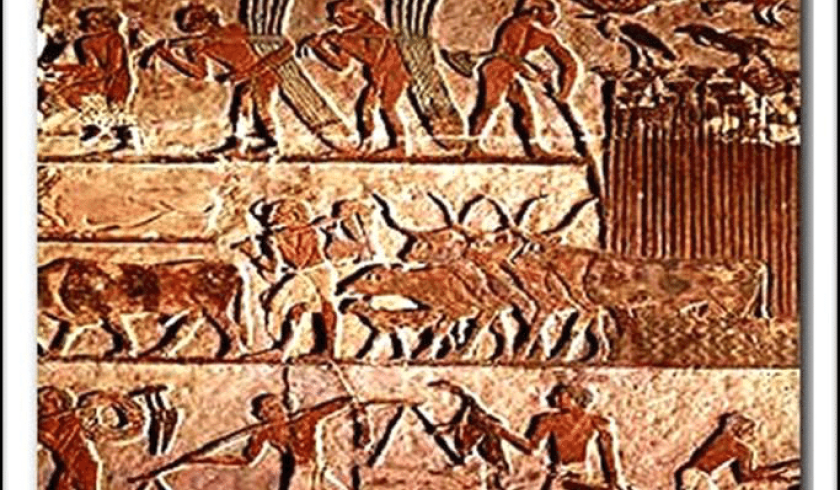

One of the first societies in history to engage in extensive agricultural production was the Indus Valley Civilization. The area was perfect for farming due to its rich soil and regular monsoon rainfall. The inhabitants of the Indus Valley Civilization were expert cultivators and possessed an advanced irrigation system.
Based on archeological evidence, it is believed that the Indus valley civilization used the crop rotation method. This preserved soil fertility and stopped the spread of pests and illnesses.
Trade and Commerce
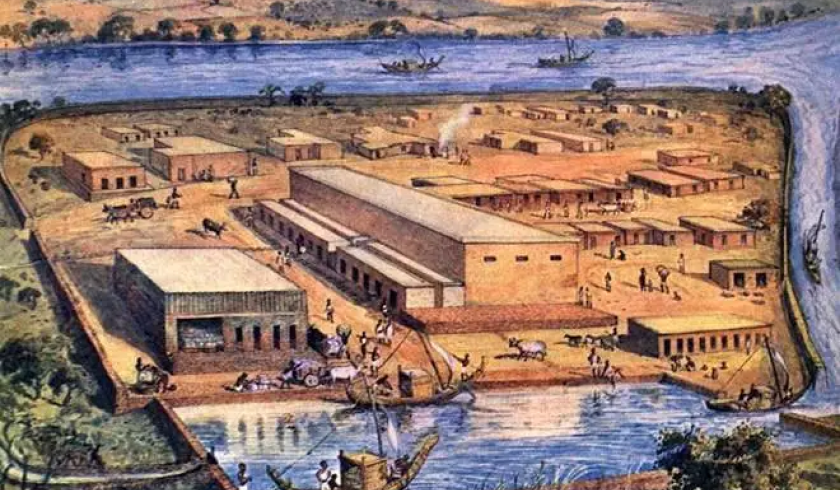

Trade in commodities like cotton, gold, and precious stones took place all over the Indus Valley Civilization, which had an intricate system of commerce and business. Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro were significant commercial hubs, and it has been discovered that they traded with Mesopotamia and other cultures. This demonstrates the highly developed economic capabilities of this civilization’s inhabitants.
Artistic Achievements
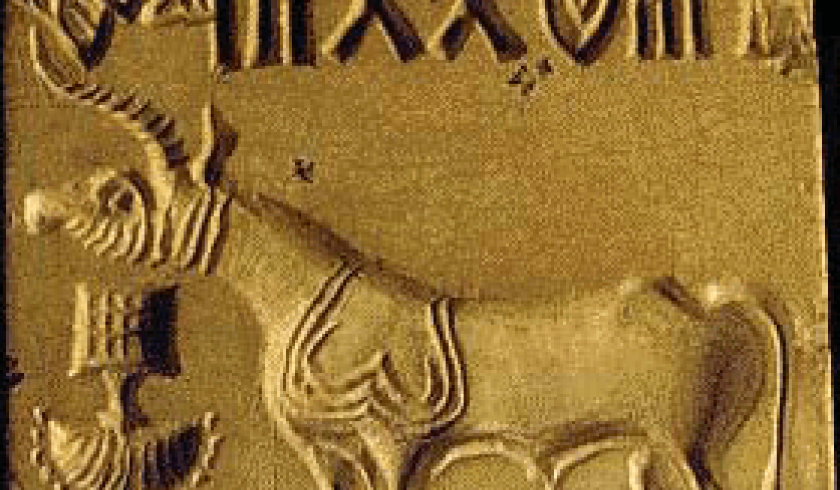

The Indus Valley Civilization was renowned for its intricate and beautiful pottery, often featuring geometric patterns and animal motifs. This civilization’s inhabitants also produced a wide range of other works of art, such as sculptures, jewelry, and stamps.
The Indus Valley Civilization is best known for its seals, made of steatite, a soft stone that was easy to carve. These seals were used for various purposes, including marking property and goods, and were often decorated with intricate designs and inscriptions. This civilization’s artistic accomplishments are proof of its people’s talent and ingenuity.
Peaceful Society

Archeologists believe the Indus Valley Civilization was peaceful, with few signs of warfare or strife. In comparison, other prehistoric societies, including the Egyptians and the Mesopotamians, were renowned for their military prowess.
According to archeological evidence, the Indus Valley Civilization constituted a highly organized government with a central authority that supervised the management of cities and towns. This might have lessened conflicts between various communities and organizations.
Decline and Disappearance
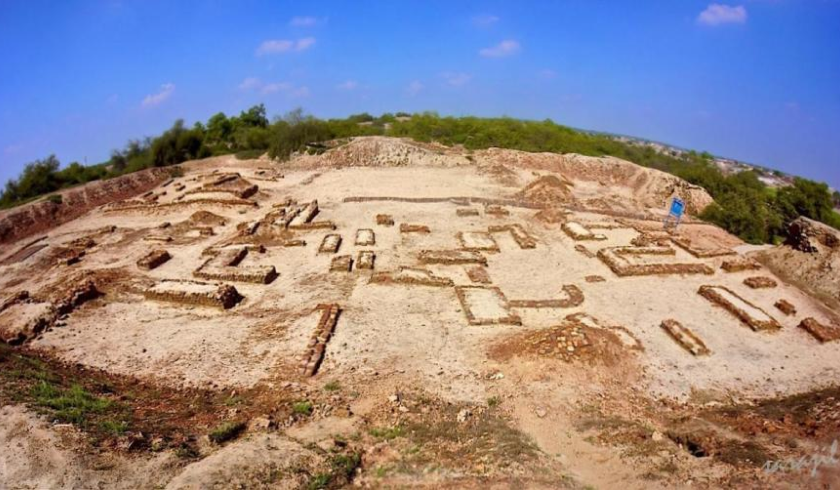

Around 1900 BCE, the Indus Valley Civilization declined and eventually vanished. According to some hypotheses, ecological factors or climate change may have had an impact. Some believe the Indus Valley Civilization may have been invaded or conquered by outside forces, such as the Aryans, who are believed to have migrated into the region around 1500 BCE.
Some scholars have suggested that the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization may have resulted from internal factors, such as political instability or economic decline, rather than external factors.
Conclusion
To sum up, the Indus Valley culture was a remarkable development in human culture. Its sophisticated writing system, advanced agriculture, and artistic accomplishments are examples of its advanced municipal planning, creativity, and skill. The Indus Valley Civilization’s influence is still seen in contemporary Indian society, despite its decline and disappearance. Learning about this prehistoric society and the mysteries that persist about this civilization is incredibly intriguing.